A novel strategy for the identification of antigens that are recognised by bovine MHC class I restricted cytotoxic T cells in a protozoan infection using reverse vaccinology
- Research
- Open Access
A novel strategy for the identification of antigens that are recognised by bovine MHC class I restricted cytotoxic T cells in a protozoan infection using reverse vaccinology
- Received: 30 November 2006
- Accepted: 09 February 2007
- Published: 09 February 2007
Abstract
Background
Immunity against the bovine protozoan parasite Theileria parva has previously been shown to be mediated through lysis of parasite-infected cells by MHC class I restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. It is hypothesized that identification of CTL target schizont antigens will aid the development of a sub-unit vaccine. We exploited the availability of the complete genome sequence data and bioinformatics tools to identify genes encoding secreted or membrane anchored proteins that may be processed and presented by the MHC class I molecules of infected cells to CTL.
Results
Of the 986 predicted open reading frames (ORFs) encoded by chromosome 1 of the T. parva genome, 55 were selected based on the presence of a signal peptide and/or a transmembrane helix domain. Thirty six selected ORFs were successfully cloned into a eukaryotic expression vector, transiently transfected into immortalized bovine skin fibroblasts and screened in vitro using T. parva-specific CTL. Recognition of gene products by CTL was assessed using an IFN-γ ELISpot assay. A 525 base pair ORF encoding a 174 amino acid protein, designated Tp2, was identified by T. parva-specific CTL from 4 animals. These CTL recognized and lysed Tp2 transfected skin fibroblasts and recognized 4 distinct epitopes. Significantly, Tp2 specific CD8+ T cell responses were observed during the protective immune response against sporozoite challenge.
Conclusion
The identification of an antigen containing multiple CTL epitopes and its apparent immunodominance during a protective anti-parasite response makes Tp2 an attractive candidate for evaluation of its vaccine potential.
Keywords
- Schizont Stage
- East Coast Fever
- 51Chromium Release Assay
- Reverse Vaccinology
- Host Cell Cytosol
Background
Theileria parva is a tick-transmitted haemoprotozoan parasite that causes an acute and often fatal disease of cattle termed East Coast fever (ECF). ECF continues to be a major threat to smallholder farmers in eastern, central and southern Africa. There are at least 28 million cattle at risk, over one million animals die each year, and annual economic losses are estimated to be US$ 189 million [1]. The multinucleate schizont stage of the parasite has the remarkable ability to transform the host lymphocytes it infects into a state of uncontrolled proliferation [2]. Whilst this allows the rapid propagation of the parasite it also leads to pathology and ultimately death in susceptible animals [3]. Cattle can be immunized against infection by the simultaneous infection of animals using the tick-derived infective sporozoite stage of the parasite and treatment with long-acting tetracycline [4]. This infection and treatment regime engenders a robust and long-lasting protective immunity that is mediated by MHC class I restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) directed against the schizont-infected lymphocyte [5, 6, 7].
The post-genomics era offers an opportunity to develop new strategies for vaccine development. In particular, there has been a paradigm shift in the approach to antigen discovery as highlighted by the use of the complete genome sequence of Neisseria meningitidis to identify and test a list of candidate vaccine antigens against meningococcal meningitis [8]. The success of this approach, termed 'reverse vaccinology' coupled with the ever-growing number of bacterial and protozoan genomes being sequenced has allowed this concept to be extended to other pathogens [9, 10, 11]. Successful application of reverse vaccinology is dependent upon the availability of a high-throughput system to test candidate antigens, but it has been hampered by the lack of good in vitro correlates of immunity. Protection from disease upon challenge in small animal models is normally the only read-out available [12]. The correlation between the induction of CTL responses and immunity to T. parva offered a system with which to apply reverse vaccinology to a complex pathogen where immunity was cell-mediated.
The strategy involved analyzing the genome to identify genes encoding secreted or membrane bound proteins. Since the genes were expressed by the intra-lymphocytic schizont stage these proteins would be exposed to the host cell cytosol and hence available for presentation to CD8+ CTL through the MHC class I processing and presentation pathway. Selected genes would be screened in vitro for recognition by T. parva specific CTL. This report describes the successful application of this novel approach to identify a vaccine candidate antigen of T. parva that is the target of schizont-specific CTL from immune cattle.
Results
Screening of genes selected from genome data
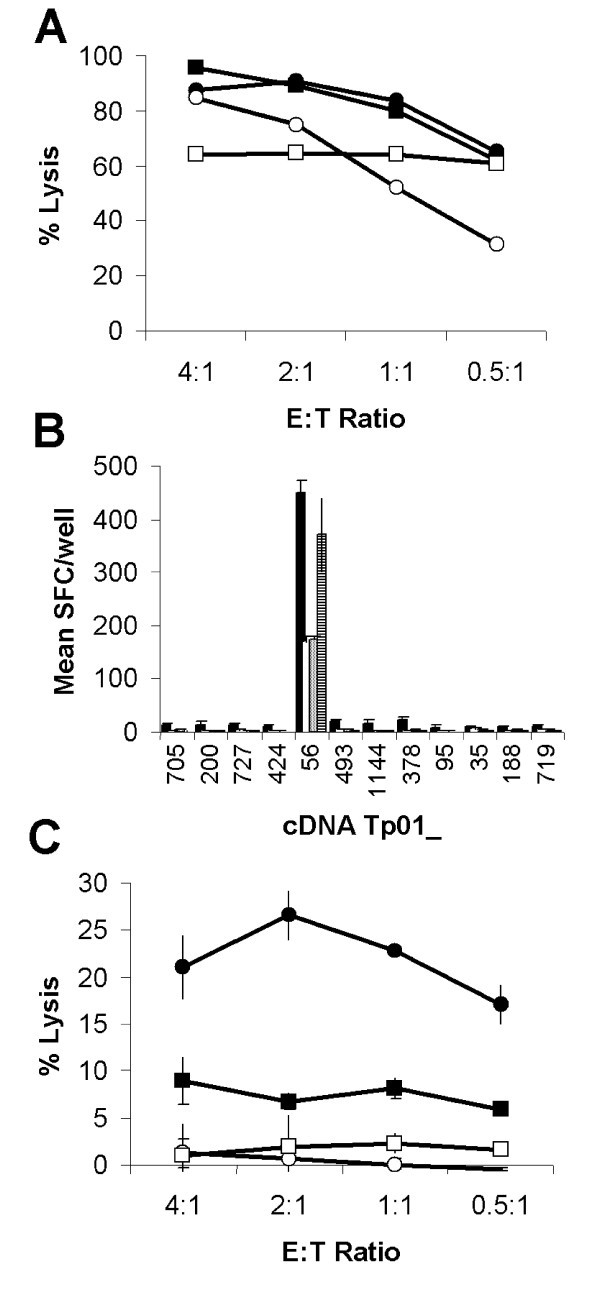
Identification of antigen Tp2. (A) Lysis of autologous schizont infected cells by four T. parva-specific CTL lines capable of (B) specifically reacting to iSF transfected with 12 selected genes as assessed by IFN-γ ELISpot and (C) lysis of cDNA Tp01_56 transfected-iSF. (A) Closed circles: BW002; open circles: BW013; closed squares: BW014; and open squares: D409. (B) IFN-γ responses to selected gene transfected iSF are presented as mean numbers of spot forming cells (SFC)/well. Black: BW002; white: BW013; grey: BW014; and hatched: D409. (C) Mean lysis of cDNA Tp01_56 transfected-iSF by CTL from the four cattle. Closed circles: cDNA Tp01_56 transfected autologous iSF; open circles: Irrelevant gene transfected autologous iSF; closed squares: cDNA Tp01_56 transfected autologous iSF pre-incubated with an anti-MHC class I mAb; and open squares: cDNA Tp01_56 transfected allogeneic iSF.
Molecular characterisation of T. parva CTL target antigen Tp2
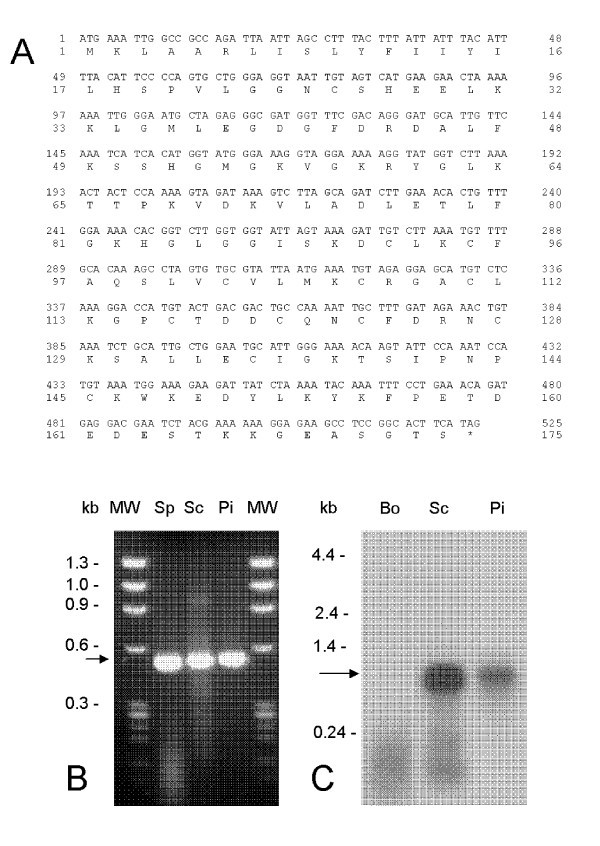
Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of antigen Tp2 fromT. parvaMuguga. (A) Tp2 is encoded by a single ORF of 525 bases translating into a protein of 174 amino acids. Transcription was assessed by (B) RT-PCR from RNA isolated from sporozoite (Sp), schizont (Sc) and piroplasm (Pi) developmental stages of T. parva and by (C) Northern blot hybridization against bovine (Bo), schizont (Sc) and piroplasm (Pi) RNA.
Mapping of CTL epitopes on Tp2
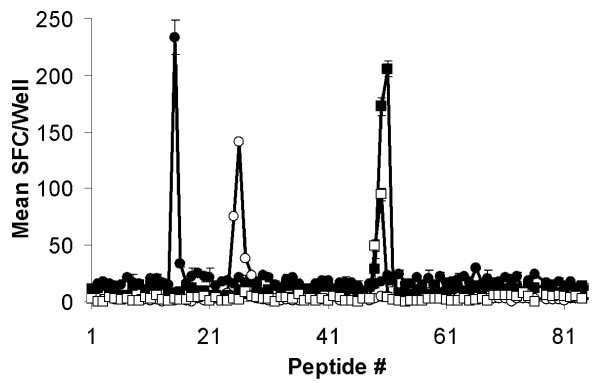
Mapping of CTL epitopes on Tp2. Eighty-four 12-mer peptides overlapping by ten amino acids encompassing the full length of Tp2 were screened with four CTL and recognition assessed by IFN-γ ELISpot. Responses are presented as mean numbers of spot-forming cells (SFC)/well. Closed circles: BW002; open circles: BW013; closed squares: BW014; and open squares: D409.
Tp2 specific responses during protective immunity
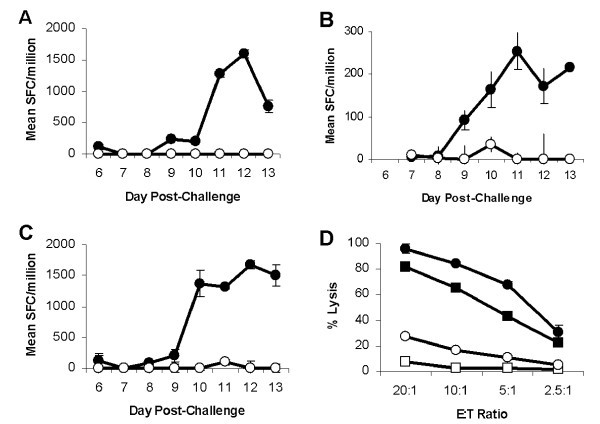
Ex vivoTp2 specific CD8+ T cell responses following challenge of immune cattle. Tp2 specific CD8+ T cell responses following challenge of T. parva immune cattle. Responses of three cattle, (A) BW014, (B) BW013 & (C) BW002, were measured longitudinally by IFN-γ ELISpot and responses are presented as mean numbers of spot-forming cells (SFC)/1 × 106 CD8+ T cells. Closed circles: Tp2 antigenic peptide and open circles: control peptide. (D) Cytotoxic activity of stimulated BW002 PBMC was assessed 14 days post-challenge. Closed circles: Autologous schizont-infected cells; closed squares: Tp2 antigenic peptide pulsed iSF; open squares: Control peptide pulsed iSF; and open circles: Allogeneic schizont infected cells.
Discussion
From the 986 predicted ORFs on chromosome 1, bioinformatics was used to select 55 genes encoding proteins that could potentially access the host cell cytosol. From the selected genes, 36 were successfully cloned into a eukaryotic expression vector and screened for recognition by schizont-specific CD8+ CTL derived from 13 cattle immunised against T. parva by a live infection and treatment immunization regime. One antigen, termed Tp2, was identified by CTL from 4 different animals. Subsequent analysis has defined multiple CTL epitopes on this molecule. Further evidence of the status of Tp2 as a bovine CTL target antigen was provided by the temporal correlation of detectable Tp2 specific CD8+ T cell responses with the onset and clearance of T. parva schizont parasitosis following challenge infection.
The success of this approach has been underpinned by the development of a sensitive CTL screening assay with which to detect recognition of the selected antigens expressed by transiently transfected antigen-presenting cells. The current screening system is based on the same principle as an assay developed to identify target antigens of melanoma tumor cell specific human CTL [19, 20]. This system utilized the WEHI TNF-α bioassay to detect CTL recognition of COS-7 cells co-transfected with pools of melanoma cell cDNA and appropriate HLA class I cDNA [19, 20]. The limited number of cloned full length BoLA class I cDNA and the relative insensitivity of WEHI cells to bovine TNF-α meant that an alternative antigen-presenting cell and read-out system were required to screen for T. parva antigens with bovine CTL. Autologous bovine skin fibroblasts stably transfected with the large T antigen of SV40 provided a system that did not limit the BoLA haplotypes that could be recruited for screening, avoided the practical limitations of working with primary cell lines and gave significantly enhanced expression of proteins following transient transfection. All bovine schizont-specific CTL lines tested to date secrete IFN-γ and detection of this cytokine using an ELISpot assay [21] provided an extremely sensitive read-out to replace the TNF bioassay. Screening of the selected genes with schizont-specific CTL identified cDNA Tp01_56 as encoding a target antigen. We subsequently confirmed that recognition was MHC class I restricted and led to lysis of the expressing cell. Despite the relative inefficiency of transient transfection, 51Chromium release assays could be performed to confirm MHC class I restricted lysis of Tp2 transfected cells.
A strength of this approach is the ability to use schizont-specific CTL populations that have been maintained in the laboratory to screen for antigens. However, although CTL lines present a sensitive and exquisitely specific screening tool there is the possibility that the antigens that will be identified will be the most immunodominant as a result of biases introduced during the in vitro restimulation procedure that is required to maintain the lines. The antigens identified may represent those that are well expressed in schizont-infected cell lines in vitro and may have little relevance to protective CTL responses in vivo. As a prelude to testing this hypothesis directly with challenge protection experiments, an experiment was conducted to look at Tp2-specific CD8+ T cell responses following the challenge of immune animals with a lethal dose of sporozoites. Both, the kinetics of the response, observed from day 9 post-challenge, and the magnitude of the response, with a responder frequency of 1/500, correlates very well with that previously described for schizont-specific CTL in efferent lymph and peripheral blood following challenge of immune cattle [5] and provides evidence to support a role for Tp2 in protective immunity. To this end, in a preliminary immunization and challenge cattle experiment evaluating Tp2 and other candidates, it was demonstrated that this CTL target antigen has potential for vaccine exploitation [16].
The ultimate vaccine against T. parva will almost certainly need to incorporate multiple antigens and epitopes in order to confer protection in the genetically diverse out-bred cattle population exposed to challenge by antigenically diverse parasite populations in the field. This study demonstrates proof of concept for the application of a genomic approach for identification of candidate antigens for inclusion in vaccines designed to induce CTL-based protection. This approach compliments the random screening of cDNA libraries that has successfully been applied to identify additional CTL target antigens from T. parva [16] and human melanomas [19, 20]. The major challenge remains the formulation and delivery of these antigens in a manner that adequately primes protective memory CD8+ T cell populations in vivo.
Conclusion
This study validates the exploitation of genomic data to identify vaccine candidate antigens from a complex haemoprotozoan parasite using CTL derived from the natural ruminant host. Extension of this approach to the complete genome of T. parva using CTL restricted by additional bovine haplotypes is likely to result in identification of further vaccine candidates. The identification of an antigen containing multiple CTL epitopes makes Tp2 an attractive candidate for inclusion in a CTL targeted sub-unit vaccine and also for the study of polymorphism in CTL epitopes in cattle and Cape buffalo (Syncerus caffer). An in-depth evaluation of this antigen in cattle involving a range of antigen delivery technologies perceived to have the potential to induce bovine CTL is in progress in order to assess the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of Tp2 against clinical East Coast fever
Methods
Generation of selected gene list
Preliminary contigs of the T. parva genome were searched against a non-redundant database of proteins extracted from GenBank. The search results were used to produce a set of putative T. parva genes that encoded highly conserved eukaryotic genes. This set of genes was complemented with a number of full length genes isolated from a cDNA library made from purified schizonts and were used to train the gene finding programs GlimmerM [14] and Phat [15], which were subsequently run against all of the preliminary contigs to produce gene models for the entire preliminary genome sequence. The proteins encoded by the predicted T. parva genes on chromosome 1 were searched against a non-redundant protein database using WU-BLAST [22], and predictions of signal peptides and signal anchors [23] and transmembrane domains [24] analysed. The results were reviewed and a set of 55 genes encoding candidate antigens was selected for cloning and screening [16].
Cloning of selected genes
Open reading frames (ORFs) less than 3.1 kb were successfully amplified by OneStep RT-PCR kit (QIAGEN Ltd., Crawley, UK) using RNA purified from T. parva (Muguga) schizont-infected lymphoblasts. Thermal cycles were: Genes up to 1 kb: 50°C 30 minutes; 95°C 15 minutes; 94°C 30 seconds; 55°C 30 seconds; 72°C 1 minute; 35 times from 94°C cycle and finally 72°C 10 minutes. Genes between 1 and 2 kb: 50°C 30 minutes; 95°C 15 minutes; 94°C 1 minute; 55°C 1 minute; 72°C 1 minute; 35 times from 94°C cycle and finally 72°C 10 minutes. Genes between 2 and 3 kb: 45°C 30 minutes; 95°C 15 minutes; 94°C 10 seconds; 55°C 1 minute; 68°C 3 minutes; 35 times from 94°C cycle and finally 68°C 10 minutes. Amplified genes were purified from agarose gels by QIAquick Gel Extraction kit (QIAGEN) and cloned into eukaryotic expression T-vector pTargeT (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Ligated samples were electroporated into JM109, and colonies were screened by PCR using gene specific internal forward primers and vector specific reverse primer (5'GAGCGGATAACATCACACAGG3'). Positive colonies were cultured in 2 ml and plasmids purified by QIAprep Spin Miniprep kit (QIAGEN) and sequenced by ABI PRISM 377 DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Although 51 of 55 selected genes were amplified, 36 were cloned successfully in pTargeT [16]. Some of the genes were consistently cloned in wrong orientation suggesting the gene products were toxic to E. coli. Some genes were amplified by the reverse primer only and missed the 5' end.
Analysis of the temporal expression of Tp2
Total RNA from sporozoites, schizonts and piroplasms was reverse-transcribed into ss-cDNA by reverse transcriptase using oligo-(dT) as primer following the recommendation of the supplier (Invitrogen). After removal of RNA complementary to the cDNA by treatment with RNase H and purification with phenol-chloroform, the ss-cDNA was PCR-amplified in the presence of specific primers used to generate the Tp2 ORF (5'-ATGAAATTGGCCGCCAGA-3' and 5'-CTATGAAGTGCCGGAGGCTTCTCC-3'). Northern blots of RNA from the schizont and piroplasm stages of T. parva were probed with the Tp2 ORF DNA fragment. This probe was also used to screen a schizont cDNA library and restriction enzyme analysis was performed by digestion with Eco RI and Bam HI.
Infection and treatment immunization of cattle and generation of CTL
All animal experimentation was reviewed and approved by the ILRI Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Four Boran (Bos indicus), 1 Jersey (Bos taurus), 1 Holstein-Friesian (Bos taurus) and 4 crossbreds, selected on the basis of BoLA type, were immunized against T. parva Muguga stock, challenged after 3 months and schizont-specific polyclonal CTL lines and clones established as described [16].
Transient transfection of immortalized skin fibroblasts
Immortalized skin fibroblasts (iSF) were transfected in 96-well plates with cDNA clones (100 ng/well) using Fugene-6 (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) and cultured for 24 hours.
IFN-γ ELISpot and 51Chromium release assays
Transfectants were co-cultured with schizont-specific CTL and recognition assessed using an IFN-γ ELISpot assay [16]. Transfectants and schizont-infected cells were labelled with 51Chromium (Amersham Biosciences Europe GmbH, Freiburg, Germany) and lysis by schizont-specific CTL lines assessed [25].
Identification of CTL epitopes with synthetic peptides
A peptide library of Tp2 was generated that contained every 12 mer, 11 mer, 10 mer and 9 mer offset by 2 amino acids from the protein sequence (Cleaved PepSet; Mimotopes, Clayton, Australia). Peptides were prepared by truncations of 12 mers at the N-terminus and supplied lyophilized with each tube containing a nominal 12 mer and the 9, 10, 11 mer truncations with the same C-terminus. Peptides were dissolved in 400 μl 50% (v/v) DNA synthesis grade acetonitrile/water (Applied Biosystems). Peptides were further diluted to 10 μg/ml in complete RPMI-1640 and 10 μl added to triplicate wells of an ELISpot plate. Autologous iSF were adjusted to a density of 4 × 105/ml and 50 μl added to wells containing peptides. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 1 hour before 50 μl of CTL at a density of 2 × 105/ml were added to each well. Plates were incubated and developed as described above. Based on the results of screening the peptide library, individual 8, 9, 10 or 11 mer peptides were synthesized and tested as described above. Peptide-pulsed iSF were prepared as targets for 51Chromium release assays by overnight incubation with peptide at 1 μg/ml in complete DMEM. Cells were harvested, labelled and assayed as described above.
Ex vivo detection of Tp2 specific CD8+ T cell responses
Immune cattle, BW002, BW013 and BW014, whose schizont-specific CTL had recognized Tp2, were challenged with a lethal dose of T. parva (Muguga) sporozoites and bled daily from day 6 to 13 post-challenge. CD8+ T cells and CD14+ monocytes were purified from PBMC by MACS magnetic cell sorting according to the manufacturer's instructions (Miltenyi Biotec, Gergisch Gladbach, Germany). CD8+ T cells were sorted indirectly using a monoclonal antibody specific for bovine CD8 (IL-A105; ILRI, Nairobi, Kenya) followed by incubation with goat anti-mouse IgG microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec). CD14+ monocytes were sorted directly by incubation with CD14 microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec). CD8+ T cells (2.5 × 105/well) and CD14+ monocytes (2.5 × 104/well) were added to IFN-γ ELISpot plates containing Tp2 peptides (1 μg/ml final concentration) and were incubated and developed as described [21]. To recall Tp2 specific CTL responses, PBMC were stimulated with autologous infected lymphoblasts 14 days post-challenge, viable cells were harvested 7 days post-stimulation and lytic activity against infected lymphoblasts and Tp2 peptide pulsed iSF assessed as described above.
Statistical analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for the analysis of fixed effects on different traits using SAS Release 8.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, USA).
Declarations
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge the contribution of all the technical staff of the ECF Vaccine Project at ILRI excellent technical input and to staff of the ILRI large animal and tick units for excellent animal husbandry and provision of parasites. We thank the Biometrics Unit, ILRI, for advice on statistical analysis. This work was funded with Grant No R8042 from the Department for International Development, UK. This is ILRI publication no 200690. YH was partly supported by the Foreign Affairs Department of the Japanese Government.
Authors’ Affiliations
References
- Mukhebi AW: Economic impact of theileriosis and its control in Africa. The Epidemiology of Theileriosis in Africa (Edited by: Norval RA, Perry BD, Young AS). London: Academic Press 1992, 379–403.Google Scholar
- Hulliger L, Wilde JKH, Brown CGD, Turner L: Mode of multiplication of Theileria in cultures of bovine lymphocytic cells. Nature 1964, 203:728–730.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Irvin AD, Morrison WI: Immunopathology, immunology and immunoprophylaxis of Theileria infections. Immune Responses in Parasitic Infections: Immunology, Immunopathology and Immunoprophylaxis (Edited by: Soulsby EJL). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press 1987, 223–274.Google Scholar
- Radley DE, Brown CGD, Burridge MJ, Cunningham MP, Kirimi IM, Purnell RE, Young AS: Chemoprophylactic immunisation of cattle against Theileria parva (Muguga) and five Theileria strains. Vet Parasitol 1975, 1:35–41.View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- McKeever DJ, Taracha ELN, Innes EL, MacHugh ND, Awino E, Goddeeris BM, Morrison WI: Adoptive transfer of immunity to Theileria parva in the CD8+ fraction of responding efferent lymph. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994, 91:1959–1963.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taracha ELN, Goddeeris BM, Morzaria SP, Morrison WI: Parasite strain specificity of precursor cytotoxic T cells in individual animals correlates with cross-protection in cattle challenged with Theileria parva . Infect Immun 1995, 63:1258–1262.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- McKeever DJ, Taracha ELN, Morrison WI, Musoke AJ, Morzaria SP: Protective immune mechanisms against Theileria parva: evolution of vaccine development strategies. Parasitol Today 1999, 15:263–267.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pizza M, Scarleto V, Masignani V, Giuliani MM, Arico B, Comanducci M, Jennings GT, Baldi L, Bartolini E, Capecchi B, Galeotti CL, Luzzi E, Manetti R, Marchetti E, Mora M, Nuti S, Ratti G, Santini L, Savino S, Scarselli M, Storni E, Zuo P, Broeker M, Hundt E, Knapp B, Blair E, Mason T, Tettelin H, Hood DW, Jeffries AE, Saunders NJ, Granoff DM, Venter JC, Moxon ER, Grandi G, Rappuoli R: Identification of vaccine candidates against serogroup B meningococcus by whole-genome sequencing. Science 2000, 287:1816–1820.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ross BC, Czajkowski L, Hocking D, Margetts M, Webb E, Rothel L, Patterson M, Agius C, Camuglia S, Reynolds E, Littlejohn T, Gaeta B, Ng A, Kuczek ES, Mattick JS, Gearing DG, Barr IG: Identification of vaccine candidate antigens from a genomic analysis of Porphyromona gingivalis . Vaccine 2001, 19:4135–4142.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alemeida R, Norrish A, Levick M, Vetrie D, Freeman T, Vilo J, Ivens A, Lange U, Stober C, McCann S, Blackwell JM: From genomes to vaccines: Leishmania as a model. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 2002, 357:5–11.View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Montigiani S, Falugi F, Scarselli M, Finco O, Petracca R, Galli G, Mariani M, Manetti R, Agnusdei M, Cevenini R, Donati M, Nogaroto R, Norais N, Garaguso I, Nuti S, Saletti G, Rosa D, Ratti G, Grandi G: Genomic approach for analysis of surface proteins in Chlamydia pneumoniae . Infect Immun 2002, 70:368–379.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Masignani V, Rappuoli R, Pizza M: Reverse vaccinology: a genome-based approach for vaccine development. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2002, 2:895–905.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gardner MJ, Bishop R, Shah T, de Villiers EP, Carlton JM, Hall N, Ren Q, Paulsen IT, Pain A, Berriman M, Wilson RJM, Sato S, Ralph SA, Mann DJ, Xiong Z, Shallom SJ, Weidman J, Jiang L, Lynn J, Weaver B, Shoaibi A, Wasawo D, Crabtree J, Wortman JR, Haas B, Angiuoli S, Creasy T, Lu C, Suh B, Silva J, Utterbacl T, Feldblyum T, Pertea M, Allen J, Taracha E, Salzberg SL, White O, Fitzhugh HA, Morzaria S, Venter JC, Fraser CM, Nene V: Genome sequence of Theileria parva , a bovine pathogen that transforms lymphocytes. Science 2005, 309:134–137.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Salzberg SL, Pertea M, Delcher A, Gardner MJ, Tettelin H: Interpolated Markov models for eukaryotic gene finding. Genomics 1999, 59:24–31.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cawley SE, Wirth AI, Speed TP: Phat – a gene finding program for Plasmodium falciparum . Mol Biochem Parasitol 2001, 118:167–174.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Graham SP, Pellé R, Honda Y, Mwangi DM, Tonukari NJ, Yamage M, Glew EJ, Bishop R, de Villiers EP, Shah T, Abuya E, Awino E, Gachanja J, Luyai AE, Mbwika F, Muthiani AM, Ndegwa DM, Njahira M, Nyanjui JK, Onono FO, Osaso J, Saya RM, Wildmann C, Fraser CM, Maudlin I, Gardner MJ, Morzaria SP, Loosmore S, Gilbert SC, Audonnet JC, van der Bruggen P, Nene V, Taracha ELN:Theileria parva candidate vaccine antigens recognized by immune bovine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006, 103:3286–3291.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bishop R, Shah T, Pellé R, Hoyle D, Pearson T, Haines L, Brass A, Hulme H, Graham SP, Taracha EL, Kanga S, Lu C, Hass B, Wortman J, White O, Gardner MJ, Nene V, de Villiers EP: Analysis of the transcriptome of the protozoan Theileria parva using MPSS reveals that the majority of genes are transcriptionally active in the schizont stage. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33:5503–5511.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schneider I, Haller D, Seitzer U, Beyer D, Ahmed JS: Molecular genetic characterization and subcellular localization of a putative Theileria annulata membrane protein. Parasitol Res 2004, 94:405–415.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Coulie PG, Brichard V, Van Pel A, Wolfel T, Schneider J, Traversari C, Mattei S, De Plaen E, Lurquin C, Szikora JP, Renauld JC, Boon T: A new gene coding for a differentiation antigen recognized by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes on HLA-A2 melanomas. J Exp Med 1994, 180:35–42.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- De Plaen E, Lurquin C, Lethe B, van der Bruggen P, Brichard V, Renauld JC, Coulie P, Van Pel A, Boon T: Identification of genes encoding for tumour antigens recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes. Methods 1997, 12:125–142.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taracha ELN, Bishop R, Musoke AJ, Hill AVS, Gilbert SC: Heterologous prime-boosting immunization of cattle with Mycobacterium tuberculosis 85A induces antigen-specific T-cell responses. Infect Immun 2003, 71:6906–6914.View ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Washington University BLAST Archives [http://blast.wustl.edu/]
- SignalP 3.0 Server [http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/]
- TMHMM Server v. 2.0 [http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM]
- Goddeeris BM, Morrison WI: Techniques for the generation, cloning and characterization of bovine cytotoxic T cells specific for the protozoan Theileria parva . J T Cult Methods 1998, 11:101–110.View ArticleGoogle Scholar
Copyright
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.